SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) - Send email
Email components
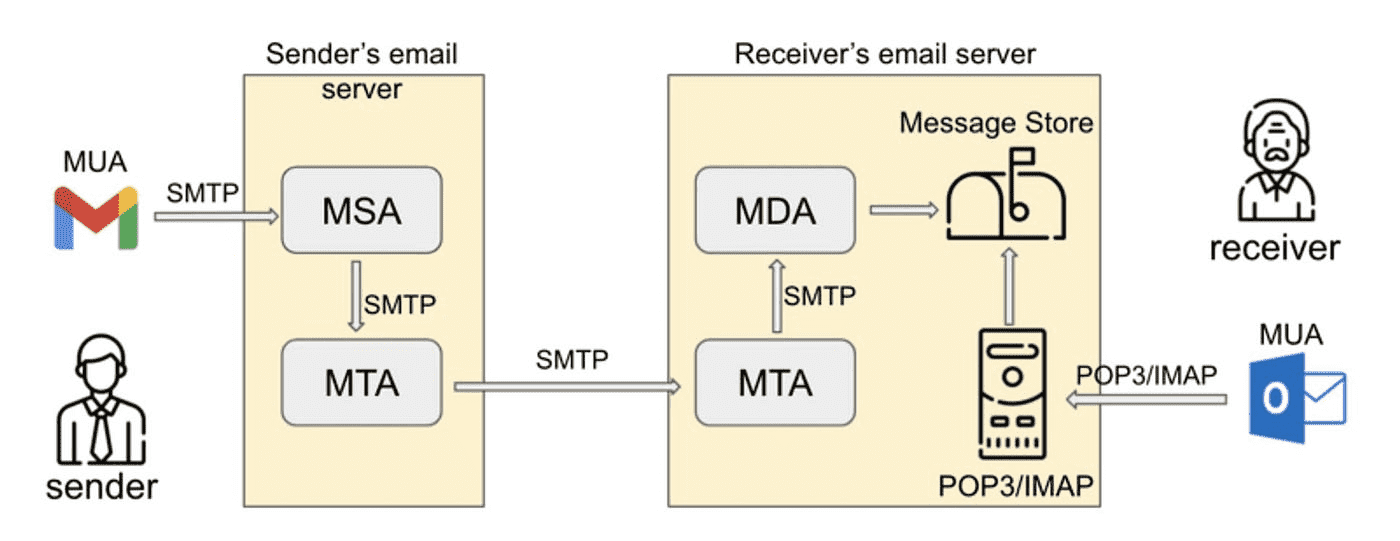
Email delivery over the Internet requires the following components: 1. Mail Submission Agent (MSA) 2. Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) 3. Mail Delivery Agent (MDA) 4. Mail User Agent (MUA)
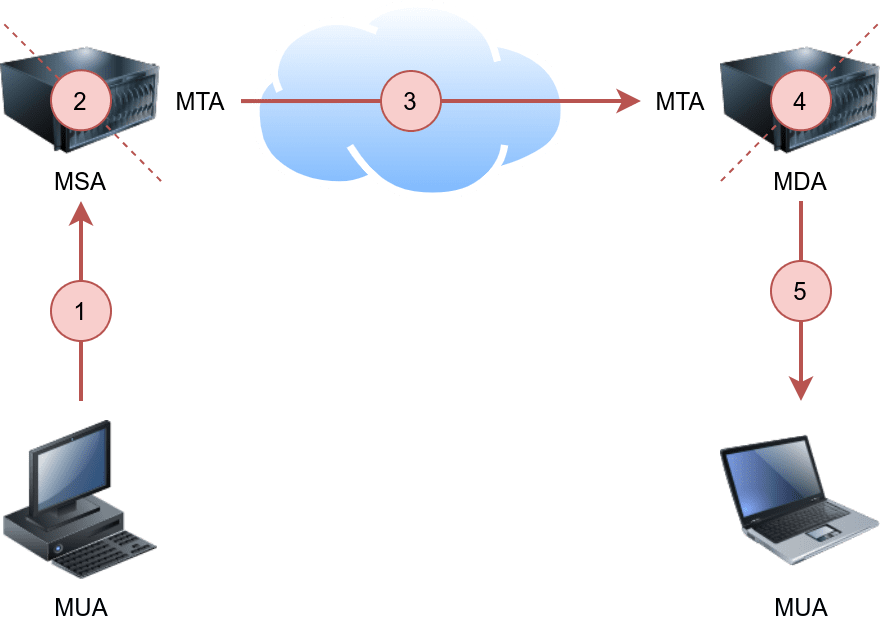
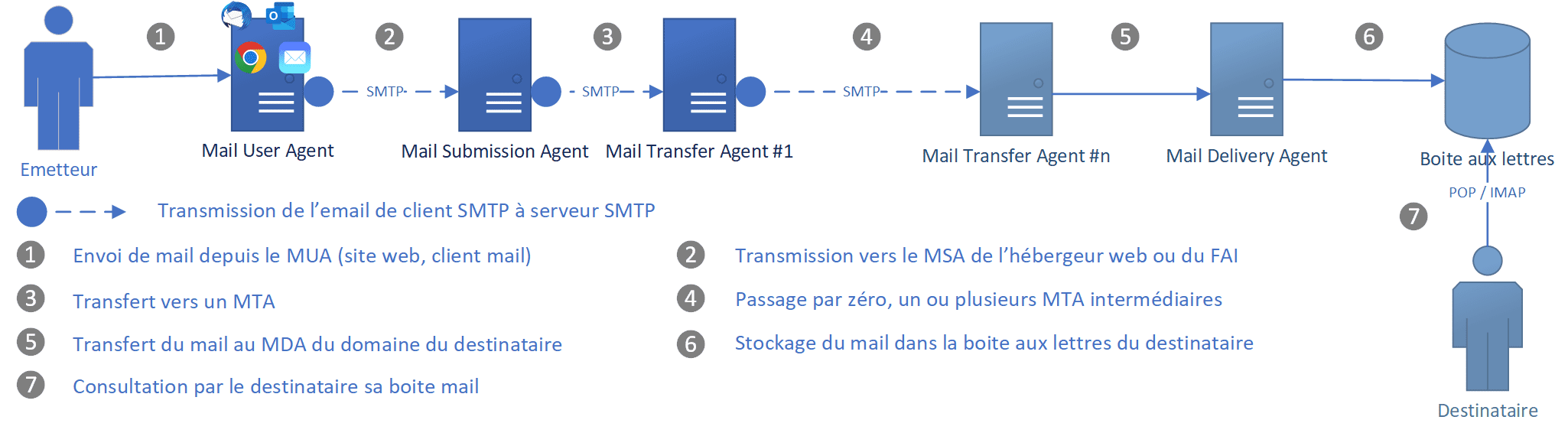
The figure shows the following five steps that an email needs to go through to reach the recipient’s inbox:
- A Mail User Agent (MUA) or simply an email client connects to a Mail Submission Agent (MSA) to send it a user's email.
- The MSA receives the message, checks for any errors before transferring it to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) server, commonly hosted on the same server.
- The MTA will send the email message to the MTA of the recipient, The MTA can also function as a Mail Submission Agent (MSA).
- A typical setup would have the MTA server also functioning as a Mail Delivery Agent (MDA).
- The recipient will collect its email from the MDA using their email client.
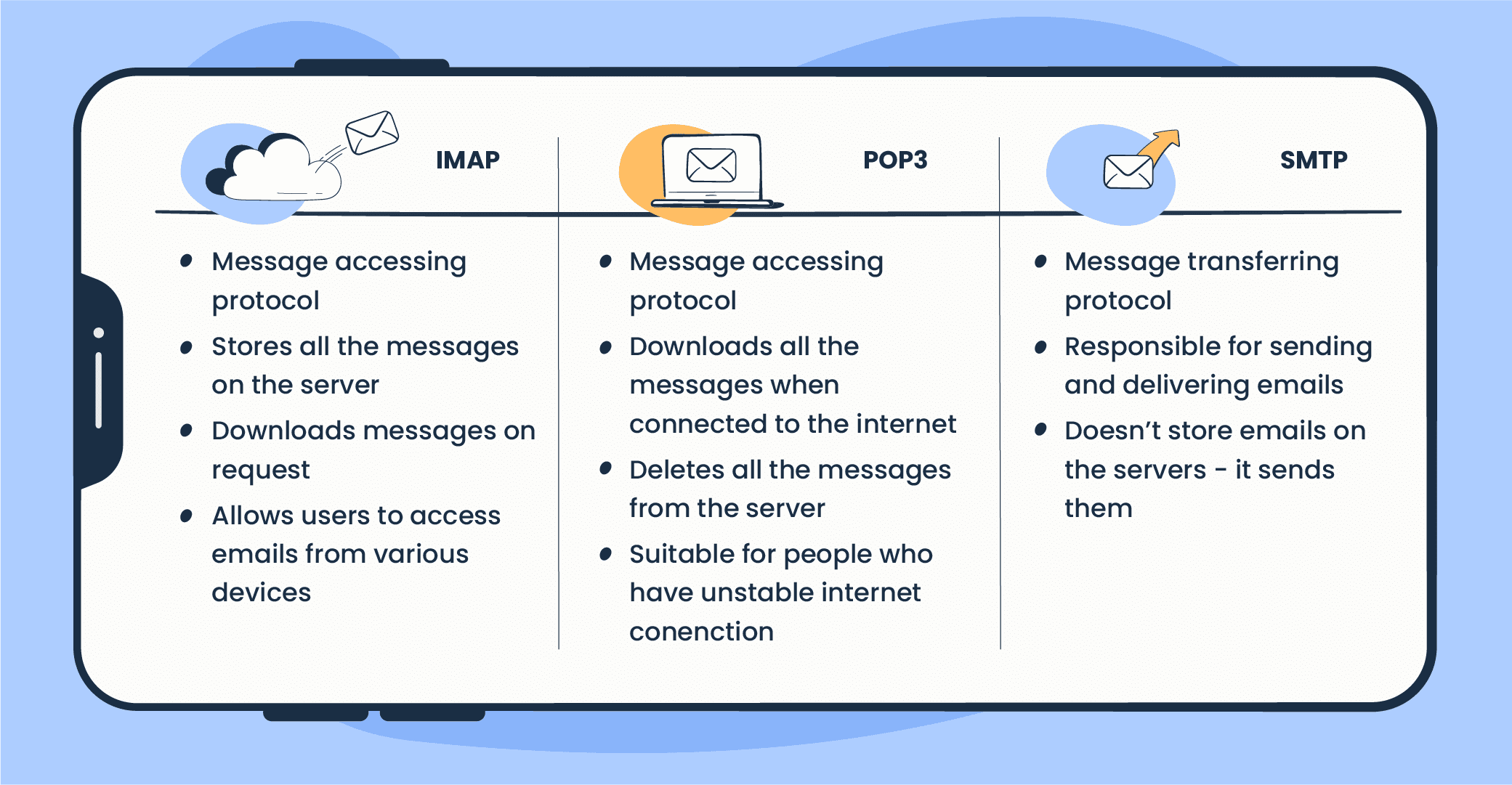
In the same way, we need to follow a protocol to communicate with an HTTP server, and we need to rely on email protocols to talk with an MTA and an MDA. The protocols are: 1. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) 2. Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3) or Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is used to communicate with an MTA server. Because SMTP uses cleartext, where all commands are sent without encryption, we can use a basic Telnet client to connect to an SMTP server and act as an email client (MUA) sending a message.
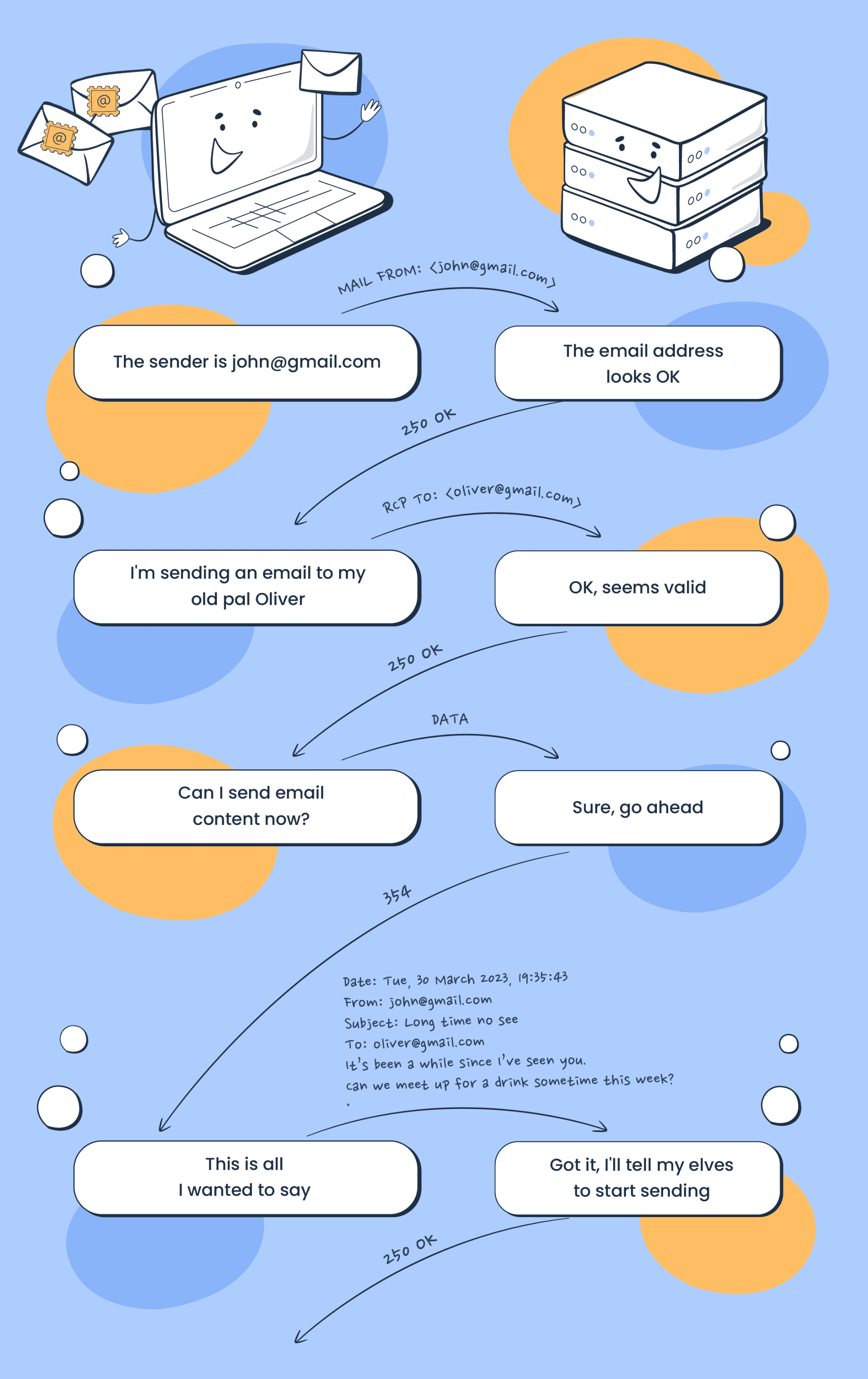
SMTP server listens on port 25 by default. To see basic communication with an SMTP server, we used Telnet to connect to it. Once connected, we issue helo hostname and then start typing our email.
telnet 10.10.45.250 25
#Trying 10.10.45.250...
#Connected to MACHINE_IP.
#Escape character is '^]'.
#220 bento.localdomain ESMTP Postfix (Ubuntu)
subject: Sending email with Telnet
Hello Frank,
I am just writing to say hi!
.
#250 2.0.0 Ok: queued as C3E7F45F06
After helo, we issue mail from:, rcpt to: to indicate the sender and the recipient. When we send our email message, we issue the command data and type our message. We issue <CR><LF>.<CR><LF> (or Enter . Enter to put it in simpler terms). The SMTP server now queues the message.
Generally speaking, we don’t need to memorize SMTP commands. The console output above aims to help better explain what a typical mail client does when it uses SMTP.
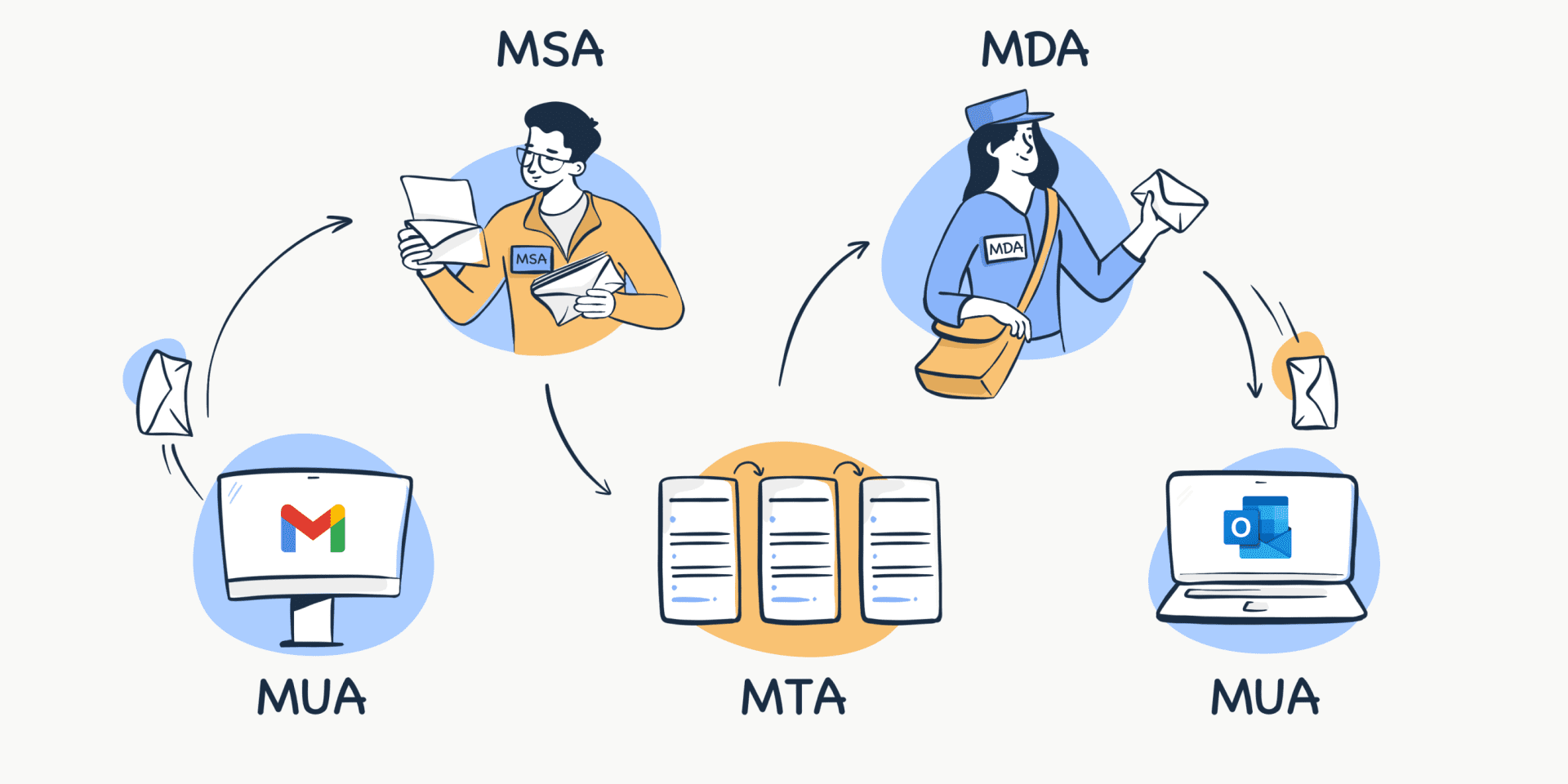
Mail Agents
There are four main agents:
- MUA (Mail User Agent) is the email client we mentioned above. It’s an application or a website that you use to send and receive email messages.
- MSA (Mail Submission Agent) receives emails from the email client, checks its headers, and verifies that the addresses are indicated correctly.
- MTA (Mail Transfer Agent) is a sendmail program that processes and transfers emails. It receives messages from the MSA. Most modern MTAs take on MSA’s responsibilities. In that case, message transfer won’t include MSAs. The most popular MTAs are Sendmail, Postfix, and Exim.
- MDA (Mail Delivery Agent) is the final agent before your emails get delivered to the recipient’s
SMTPserver and then retrieved through inbound email servers (IMAP or POP3).